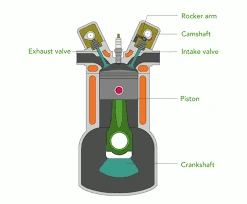
What Is Combustion in an IC Engine?
Combustion in an internal combustion (IC) engine is the process of burning fuel to generate power. In a typical IC engine, fuel (usually gasoline or diesel) is mixed with air inside the engine’s combustion chamber. When this mixture is ignited, it creates an explosion, releasing energy in the form of heat and pressure. This energy is what drives the engine’s pistons, ultimately powering the vehicle.
The Four-Stroke Combustion Cycle
Most modern internal combustion engines operate on a four-stroke cycle, which consists of four key phases: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
- Intake: The intake valve opens, allowing air and fuel to enter the combustion chamber.
- Compression: The piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
- Power (Combustion): A spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion. The expanding gases push the piston down, generating power.
- Exhaust: The exhaust valve opens, and the burned gases are expelled from the chamber, making room for the next cycle.
This process repeats hundreds of times per minute, ensuring a steady supply of power to the engine.
Types of Combustion in IC Engines
There are two main types of combustion processes in IC engines: spark-ignition and compression-ignition.
- Spark-Ignition Combustion: Common in gasoline engines, this type of combustion relies on a spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
- Compression-Ignition Combustion: Diesel engines use compression-ignition, where air is compressed to such high pressures that it heats up and ignites the fuel without the need for a spark plug.
Factors Influencing Combustion Efficiency
Efficient combustion is key to optimizing engine performance. Factors that affect combustion efficiency include:
- Fuel Quality: Higher-octane fuels burn more efficiently in spark-ignition engines, reducing knock.
- Air-Fuel Ratio: The ideal mixture of air and fuel ensures complete combustion, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Ignition Timing: Proper timing of the spark or compression affects how well the fuel burns.
- Engine Temperature: An engine operating at its optimal temperature ensures better fuel vaporization and combustion.
Why Combustion Is Important for Engine Performance
The combustion process is crucial because it directly impacts the engine’s power, fuel economy, and emissions. Incomplete combustion can lead to wasted fuel and higher emissions, while efficient combustion results in maximum power output and minimal environmental impact.
Engineers are constantly working on improving combustion efficiency through better engine designs, advanced fuel injection systems, and alternative fuels, all of which aim to make engines more powerful, cleaner, and efficient.
Q&A: Combustion in Internal Combustion (IC) Engines
Q1: What is combustion in an internal combustion (IC) engine?
A1: Combustion in an IC engine is the process of burning fuel inside the engine’s combustion chamber to produce energy. This energy is created by igniting a mixture of air and fuel, which releases heat and pressure that moves the engine’s pistons, powering the vehicle.
Q2: What are the phases of the four-stroke combustion cycle?
A2: The four-stroke combustion cycle consists of:
- Intake: Air and fuel enter the combustion chamber.
- Compression: The air-fuel mixture is compressed by the piston.
- Power (Combustion): The mixture is ignited, creating an explosion that pushes the piston down.
- Exhaust: Burned gases are expelled, and the cycle starts again.
Q3: What is the difference between spark-ignition and compression-ignition combustion?
A3:
- Spark-Ignition Combustion: Used in gasoline engines, where a spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture.
- Compression-Ignition Combustion: Found in diesel engines, where air is compressed until it becomes hot enough to ignite the fuel without a spark plug.
Q4: How does fuel quality affect combustion in IC engines?
A4: Higher-quality fuels, such as high-octane gasoline, burn more efficiently, reducing engine knock and ensuring more complete combustion. This leads to better performance, fuel economy, and lower emissions.
Q5: Why is the air-fuel ratio important in combustion?
A5: The correct air-fuel ratio ensures that there is enough oxygen to burn the fuel completely. A mixture that is too rich (more fuel than air) can lead to unburned fuel and poor efficiency, while a lean mixture (more air than fuel) may result in incomplete combustion and engine knock.
Q6: What factors influence combustion efficiency?
A6: Several factors influence combustion efficiency, including:
- Fuel quality
- Air-fuel ratio
- Ignition timing
- Engine temperature All of these factors must be optimized to ensure efficient combustion, resulting in better engine performance and lower emissions.
Q7: Why is combustion crucial for engine performance?
A7: Combustion is essential for powering the engine. Efficient combustion produces maximum power output while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions. Poor combustion can lead to wasted fuel, reduced power, and increased pollution, making it critical to optimize the process for engine performance and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Combustion in IC engines is the heart of vehicle power generation. Understanding how this process works, along with the various factors that affect it, is essential to grasping how modern engines perform and what innovations are driving the future of automotive technology.